Do you remember the days when Off-Grid lighting meant big clunky flashlights or camping lanterns? When the power went out at home and you searched the “junk drawer” to find the emergency flashlights and candles. It’s certainly not like that anymore.
In recent years, off-grid lighting has become one of the most important and accessible technologies for anyone interested in sustainability, resilience, or simply reducing their dependence on traditional utilities. Off-grid lighting refers to lighting systems that operate independently from the electrical grid, using self-contained energy sources such as solar power, rechargeable batteries, or even manual charging mechanisms. These systems have become invaluable in emergency preparedness, rural development, outdoor recreation, and modern off-grid living.
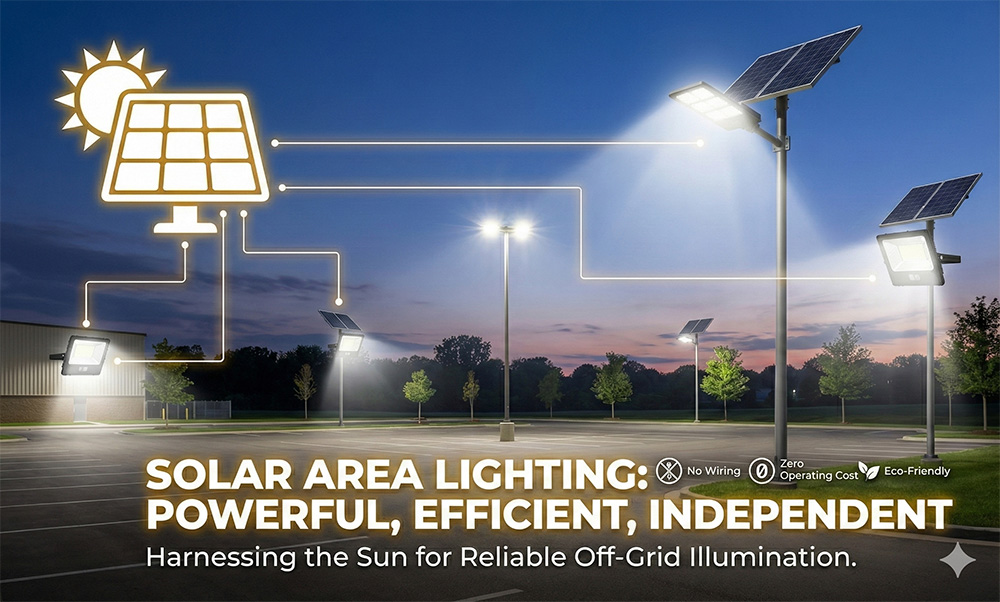
Among the most popular forms of off-grid lighting is solar lighting. Solar-powered lights work by converting sunlight into stored energy, which is then used to power efficient LED fixtures after dark. Solar post lights, lanterns, bollards and pathway lights, home lighting kits, and large-scale solar area lights and streetlights are all common examples. Because they require not trenching, no fuel, wiring, or ongoing operating costs, solar lighting offers a clean and renewable solution that continues to function even during electrical grid failures. Solar technology has improved dramatically over the past decade, making these systems brighter, more durable, and more reliable than ever before.
One of the key features of solar off-grid lighting is that there are zero operating costs making the return on the investment very attractive. An additional benefit that helps with ROI is the ease of installation. You can usually deploy the solar system yourself without running any power or using an expensive electrical contractor.
Rechargeable lighting is another key component of off-grid illumination. While it usually does require electrical power to charge the modern rechargeable lamps and systems are powered by advanced batteries such as lithium-ion, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), or nickel-metal hydride (NiMH). These batteries pair with highly efficient LEDs, allowing rechargeable table lamps, desk lamps, lanterns, flashlights, headlamps, and work lights to run for many hours on a single charge. They can be recharged through USB ports, car chargers, power banks, or solar panels, making them ideal for camping trips, job sites, remote cabins, or emergencies when the grid is unavailable. Because they eliminate the need for disposable batteries, rechargeable lights also reduce waste and long-term cost.
While less common than solar and rechargeable lighting, some people rely on hybrid systems that combine solar charging with USB or manual charging options. These multi-input lights are especially helpful in unpredictable environments, such as during storms or wilderness travel, where sunlight may be limited. In addition to solar and rechargeable technologies, some off-grid lighting devices use alternative methods like hand-crank generators, kinetic motion, or thermoelectric systems that convert heat into energy. While these are typically used as backup options, they provide an extra layer of security in situations where consistent access to sunlight or electricity cannot be guaranteed.
The applications for off-grid lighting span a wide range of environments and needs. During emergencies and natural disasters, off-grid lighting becomes essential for communication, safety, medical care, and navigation when the grid goes down. In rural or remote areas around the world, solar home lighting systems, solar area lights and solar streetlights extend productive hours into the evening, reduce reliance on dangerous kerosene lamps, and improve safety and recreational opportunities. Outdoor enthusiasts also benefit greatly from off-grid lighting, using solar lanterns and rechargeable headlamps to illuminate campsites, trails, and RV setups without the noise or fuel consumption of generators. Even homeowners in urban and suburban areas rely on solar floodlights, garden lights, and shed lighting to improve security and convenience without increasing energy bills. Parks are able to install solar lighting in areas where they can’t trench power into. Beach areas are able to add pathway lighting and area lighting to improve safety and security where they were not able to add it previously.
The importance of off-grid lighting extends beyond convenience. It represents a meaningful step toward energy independence, allowing individuals and communities to function even when the grid becomes unreliable. Environmentally, solar and rechargeable lighting reduce fossil fuel consumption, carbon emissions, and single-use battery waste. Economically, these systems offer long-term savings by eliminating fuel costs and reducing the need for frequent battery replacements. Globally, off-grid lighting has profound health and safety benefits, replacing kerosene lamps that contribute to respiratory illnesses and house fires in developing regions.
Looking ahead, the future of off-grid lighting is bright as technology continues to advance. Improvements in solar panel efficiency, battery longevity, smart controls, and durable LED fixtures will make off-grid lighting even more powerful and accessible. Whether used for emergency preparedness, sustainable architectural design, rural electrification, outdoor adventures, or everyday household needs, off-grid lighting offers clean, reliable, and resilient illumination anywhere it’s needed.